What Are Low-Code and No-Code Tools?
- No-Code platforms let you build applications using visual interfaces—drag-and-drop logic and pre-built components—without writing any code.
- Low-Code tools reduce the amount of coding needed, offering visual builders plus snippets of custom code where necessary. This hybrid makes them more flexible and scalable.
- They’re ideal for quick launches and simple tools, but they’re not an alternative to foundational software engineering.
Why It’s Easy to Get Trapped—But Should You?
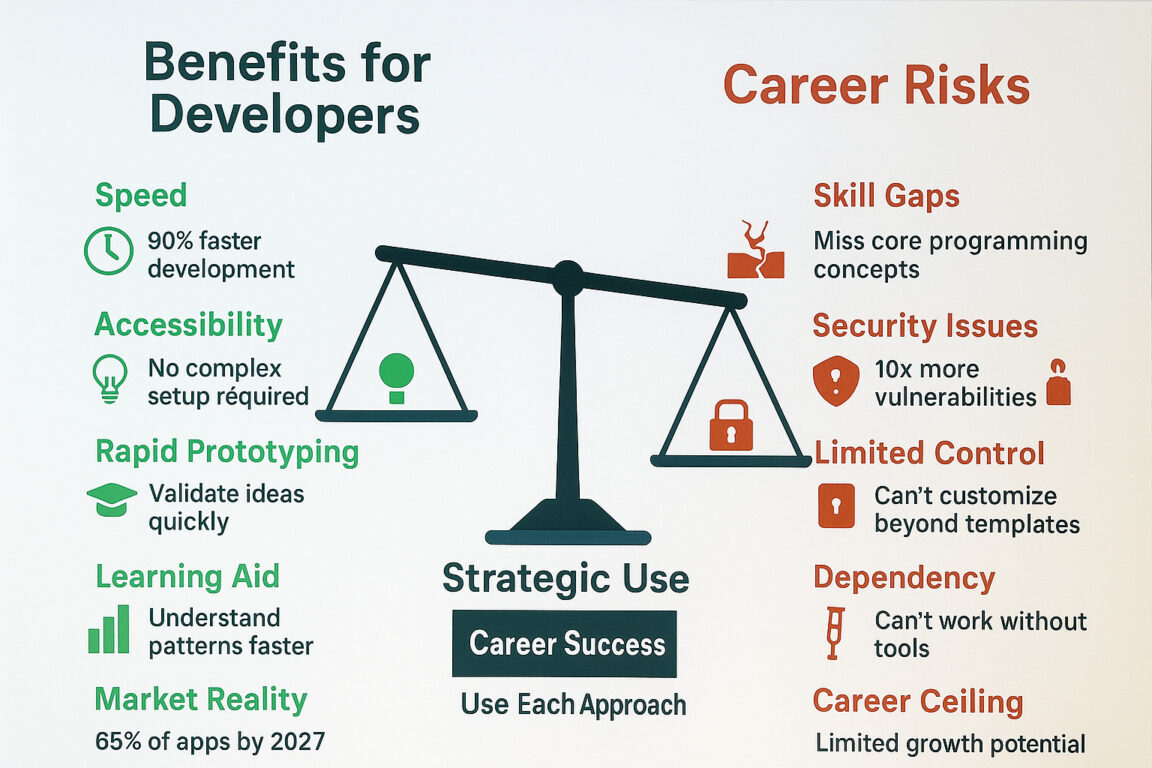
1. Speed Feels Great—Until It’s NotLow-code/no-code platforms can cut development time by up to 90%, and enterprise adoption is skyrocketing—Gartner expects 65% of new apps to use them by 2027.Yet this convenience comes at the cost of missing out on real coding mastery.
2. Early Wins vs. Long-Term SkillsThese tools often hide complexities like architecture, testing, and optimization behind pre-made modules. You may build a dashboard quickly, but not learn how HTTP requests, state, or security actually work.
3. Real Risks from AI-Generated CodeAI tools that write code—like “vibe coding” interfaces—can accelerate output, but they also introduce serious risks. A recent study found AI-assisted code-writing resulted in 10× more security vulnerabilities, including exposed secrets and misconfigurations.Without deep skill and oversight, you may inadvertently push insecure patterns into production.
A Balanced Path Forward for New Developers
Situation |
When to Use Low-Code / AI Tools |
When to Code Yourself |
| Building simple MVPs | Rapid prototyping with no-code platforms | Rewrite later using hand-coded logic |
| Learning development | Explore APIs or prototype features | Build features yourself from scratch |
| Managing enterprise tools | Low-code for internal dashboards | Learn backend APIs and secure integration |
| Improving productivity | Use AI for boilerplate or scaffolding | Always review, refactor, and optimize |
- Start with code: Learn JavaScript, HTML, CSS, and core backend logic before relying on visual tools.
- Use tools strategically: Let low-code platforms help with prototypes—but always revisit them with clean, maintainable code.
- Review AI output critically: Don’t trust code generated by AI without auditing it thoroughly.