The secret sauce for new product Development can be a matter of focus. The first step should be to figure out what your target audience is experiencing and how you can change that experience to make it better. That’s why it is important to gather customer insights through surveys, interviews, ethnographic research, and monitoring social media interactions.
Product development should be an ongoing process that encompasses all stages of a product’s life cycle, including generating ideas, validating proof of concept, prototyping, developing a minimum viable product, pre-launch preparations, and post-launch evaluations. In other words, the process of discovering and refining the product should continue throughout its entire lifespan.
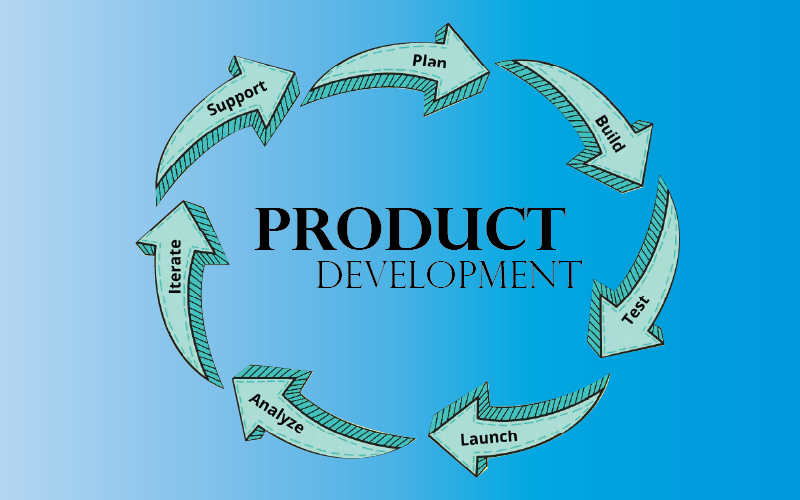
The 7 stages in product development typically include:
- Idea generation and concept development
- Market research and feasibility analysis
- Design and prototyping
- Testing and validation
- Manufacturing and production
- Distribution and marketing
- Customer support and post-sales service.
Step 1: Idea generation and concept development.
Idea generation and concept development is the first stage in the product development process. It involves identifying a need or opportunity in the market, and generating ideas for a product or service that addresses that need. This can be done through brainstorming sessions, research, customer feedback, or other methods. The goal of this stage is to develop a basic concept or prototype of the product or service that can be evaluated and refined. This stage will also involve the assessment of the feasibility of the idea, such as analyzing the market demand, technical feasibility, and the resources required to develop the product.
How to identify the issues that the target audience is facing:
There are several ways to identify the issues that the target audience is facing:
- Market research: Conducting surveys, focus groups, and interviews with potential customers can provide valuable insights into their needs, pain points, and challenges.
- Social listening: Monitoring social media platforms and online forums can give an understanding of the problems and questions that customers are discussing.
- Analyzing competitors: Examining the products and services offered by competitors can give an idea of the issues that they are addressing and what gaps may exist in the market.
- Customer feedback: Collecting feedback and reviews from existing customers can provide valuable insights into the issues they are facing and areas where they would like to see improvements.
- Industry reports and analysis: Reading industry reports, trends, and analysis can provide an understanding of the general challenges and opportunities in the market.
- Employee or stakeholder feedback: Employee or stakeholder feedback can also be valuable in understanding the issues that the target audience is facing, as they may have direct or indirect interactions with the target audience.
Step 2: Market research and feasibility analysis
Market research and feasibility analysis are the second stages in the product development process. It involves gathering and analyzing information about the market, customers, and competition in order to determine the viability of the product idea.
Market research includes activities such as surveys, focus groups, interviews, and online research to gather information about the target market, including their demographics, needs, pain points, and preferences. This information is then used to create customer personas and validate the product concept.
Feasibility analysis is the process of evaluating the potential success of the product idea by assessing factors such as market demand, technical feasibility, and the resources required to develop and bring the product to market. This can include analyzing the potential size of the market, identifying the target audience, assessing the competition, and determining the costs and potential revenue for the product.
The goal of market research and feasibility analysis is to gather sufficient information to confirm that the product concept is viable and that there is a potential market for it, before proceeding to the next stages of development.
Step 3: Design and prototyping
Design and prototyping are the third stages in the product development process. It involves creating a detailed design of the product and building a physical or digital representation of it, called a prototype.
During the design phase, the team will determine the specific features and specifications of the product, such as size, shape, materials, and functionality. They may also create visual renderings or computer-aided design (CAD) models of the product to help communicate the design to others and make any necessary revisions.
Prototyping refers to the process of creating a physical or digital representation of the product design so that it can be tested and evaluated. There are different types of prototypes, such as paper prototypes, digital wireframes, and physical mockups, that can be used depending on the stage of development and the product being developed.
The goal of design and prototyping is to create a functional representation of the product that can be tested and evaluated by customers, stakeholders, and the development team, to ensure that it meets the needs of the target audience and is technically feasible to produce.
Additionally, the design and prototyping stage also involves testing the design for manufacturability, which is the ability to manufacture the product at a reasonable cost, with high quality, and in a timely manner. This can help to identify and address any potential issues with the design that could impact the manufacturing process, such as difficult assembly or use of hard-to-source materials
Step 4: Testing and validation
Testing and validation are the fourth stages in the product development process. It involves evaluating the product prototype to ensure that it meets the requirements and specifications defined in the previous stages.
Testing can include both functional testing, to ensure that the product works as intended, and usability testing, to ensure that it is easy for the target audience to use and understand. Depending on the product, different types of testing may be required, such as performance testing, stress testing, and compatibility testing.
Validation refers to the process of ensuring that the product meets the needs of the target audience and that it complies with any relevant regulations and standards. This can include gathering feedback from customers and stakeholders and analyzing the results of testing.
The goal of testing and validation is to identify and resolve any issues or problems with the product before it goes into mass production and distribution so that it can be ensured that the product is of high quality and meets the needs of the target audience.
Step 5: Manufacturing and Production
Manufacturing and production are the fifth stages in the product development process. It involves the process of creating the final product and getting it ready for distribution to customers.
During the manufacturing phase, the product design is transformed into a final product using various methods such as assembly, molding, casting, or machining. The method used will depend on the product and the materials used. This stage will also typically involve sourcing and coordinating with suppliers and vendors who will provide the materials and components needed to manufacture the product.
Production refers to the process of assembling the final product, which can include tasks such as packaging, labeling, and quality control. This stage will also include the testing of the final product to ensure that it meets the specifications and requirements defined in the previous stages.
The goal of manufacturing and production is to create a final product that is of high quality, meets the needs of the target audience, and is ready for distribution and sale to customers.
Step 6: Distribution and marketing
Distribution and marketing are the sixth stages in the product development process. It involves getting the product to the customers and promoting it to generate awareness and sales.
Distribution refers to the process of getting the product to the customers, which can include tasks such as warehousing, logistics, and fulfillment. This stage will also include determining the most effective channels for distributing the product, such as online, retail, or through a distributor.
Marketing refers to the process of promoting a product to generate awareness and sales. This can include activities such as advertising, public relations, sales promotions, and creating a website and social media presence. The marketing plan will be developed based on the target audience, their needs and pain points, and the unique selling point of the product.
The goal of distribution and marketing is to make the product available to customers and generate interest and demand for it so that it can be successfully launched and generate revenue for the business.
Step 7: Customer support and post-sales service
Customer support and post-sales service is the final stage in the product development process. It involves providing assistance and support to customers after the product has been sold.
Customer support includes activities such as answering questions, troubleshooting problems and providing technical assistance. This can be done through various channels such as phone, email, or chat support, and it’s important that the support is easily accessible and efficient.
Post-sales service refers to the maintenance and repair of the product, if needed, and providing a warranty or guarantee for the product. This can include tasks such as providing replacement parts or servicing the product if it breaks down.
The goal of customer support and post-sales service is to ensure customer satisfaction by providing assistance and support and addressing any issues or problems that may arise with the product after it has been sold. This can help to build a positive reputation for the company and increase customer loyalty, which can lead to repeat business and positive word-of-mouth
Benefits of the New Product Development Process
The new product development process, which includes the stages of idea generation and concept development, market research and feasibility analysis, design and prototyping, testing and validation, manufacturing and production, distribution and marketing, and customer support and post-sales service, can provide several benefits for a business, some of which include:
- Increased chances of success: By following a structured process, businesses can better evaluate the viability of a product idea and identify and address potential issues before the product is launched.
- Improved customer focus: By gathering input from customers throughout the process, businesses can ensure that the product meets the needs of the target audience.
- Reduced costs: By identifying and addressing potential issues during the design and testing stages, businesses can reduce the costs associated with fixing problems during or after production.
- Faster time to market: By following a structured process, businesses can more efficiently bring new products to market.
- Improved communication and collaboration: By involving multiple teams and stakeholders in the development process, businesses can improve communication and collaboration, which can lead to more effective decision-making and better results.
- A better understanding of the market and competition: By conducting market research and feasibility analysis, businesses can gain a deeper understanding of the market, competition, and customer needs, which can help to inform future product development decisions.